In this blog post, we will explore the paper “PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation” authored by Charles Qi et al., published in CVPR in 2017. Let’s begin!
What is the Paper about?
The paper introduces the PointNet architecture that is designed to handle point cloud. As recall in the previous post, point clouds are sets of points in 3D space representing objects.
Unlike traditional deep learning methods, which need to convert the point cloud into voxels or grids before feeding them into neural networks, PointNet bypasses this step entirely. This direct processing capability is important in real-time scenarios where sensor-collected point cloud data requires rapid analysis. By eliminating the preprocessing bottleneck, PointNet enhances performance in tasks such as point cloud classification and segmentation. Figure 1 shows the tasks that PointNet can perform on.
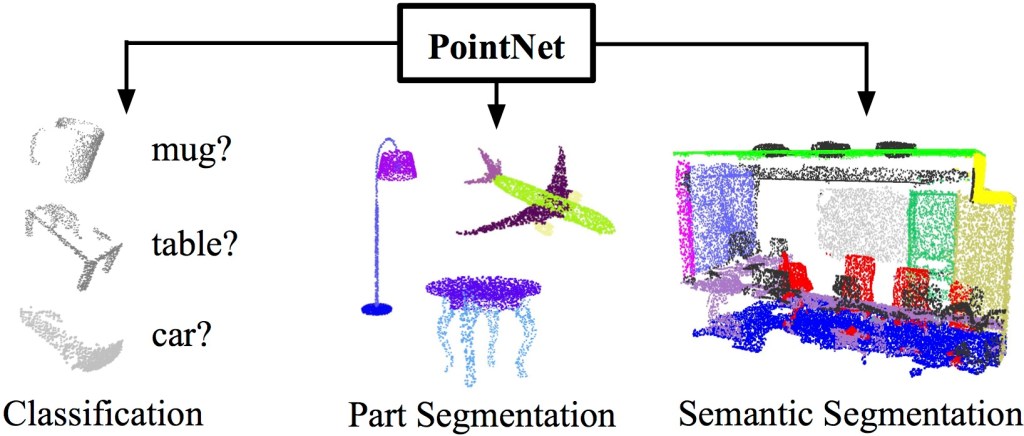
Contributions of the Paper
Several contributions of the papers are:
- Invariance to Permutations: PointNet introduces a neural network architecture that is invariant to the permutation of input points, meaning it can process point clouds regardless of the order in which points are presented.
- Transformation Invariance: The network is also capable of learning transformation invariance, enabling it to recognize objects regardless of their position, orientation, or scale in the point cloud.
- End-to-End Learning: PointNet enables end-to-end learning, allowing the model to directly process raw point clouds without requiring preprocessing steps such as voxelization or pointwise feature extraction.
The PointNet Architecture
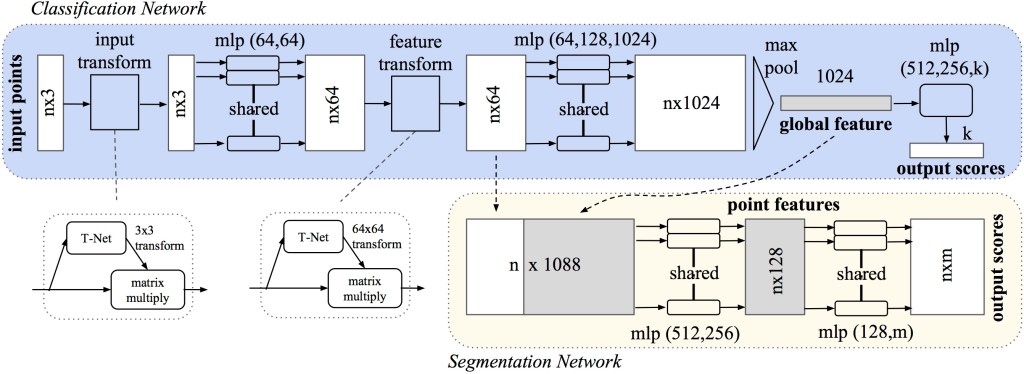
Figure 2 displays the PontNet architecutre. PointNet consists of several layers of neural networks designed to process point clouds directly. It begins with a shared multi-layer perceptron (MLP) applied independently to each point, followed by a pooling layer to aggregate information across all points. The resulting global feature vector captures the overall characteristics of the point cloud, which can then be used for various downstream tasks.
Results
The authors demonstrate the effectiveness of PointNet through extensive experiments on various tasks, including object classification, part segmentation, and scene semantic parsing. PointNet achieves state-of-the-art performance on several benchmark datasets, showcasing its ability to learn meaningful representations directly from point clouds without the need for complex preprocessing steps.
Conclusion
PointNet represents a significant advancement in the field of deep learning for 3D data processing. Its ability to directly process point clouds while being invariant to permutations and transformations makes it a versatile and powerful tool for tasks such as classification and segmentation.
***
Reference:
- Qi, C. R., Su, H., Mo, K., & Guibas, L. J. (2017). Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 652-660).
Leave a comment