Hello everyone, and welcome to the first post of the blog. This time, I aim to explain the concept of point clouds in an approachable way. So, let’s dive in.
What is a Point Cloud?
I found this video from Geospatial World’s Youtube channel helpful in understanding the concept. The video sums up that a point cloud:
- Is a set of data points in a 3D coordinate system (X, Y, Z), with each point representing a precise location in space [1]
- Creates a three-dimensional representation of an object or area [1]
- Is generated by 3D scanners that uses lasers, cameras, or sensors (mostly using Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging)) [1]
- Is used in autonomous vehicles, agriculture, surveying, mapping, aerial inspection, and construction [1]
In addition, a point cloud typically contains not only spatial coordinates (X, Y, Z), but also information like color or intensity. For example, a point in the cloud might be in the form of XYZI (I for Intensity) or XYZRGB (Red Green Blue color space).
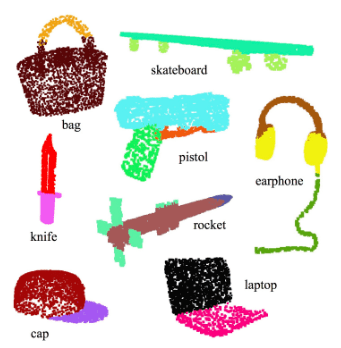
Visually, we see a point cloud as a group of dots resembling an object. Figure 1 displays various examples of objects represented by point clouds. In the picture, each dot is color coded to distinguish the parts of the object.
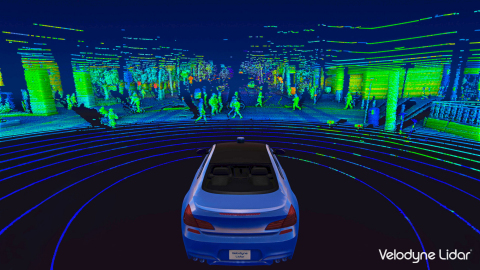
In Figure 2, a self-driving car uses Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor to get the point clouds of its surrounding. The system can use the point clouds to calculate object distances (as it contains XYZ coordinate) and identify the classes of the objects (person, traffic sign, surrounding vehicles, etc.).
What is the Application of Point Clouds?
Some application of point clouds that I find interesting are:
- Construction Progress Tracking: by capturing point clouds regularly while building progresses, you can use this data to keep track of what work is completed in an area at some given time.
- Self-Driving Car Perception: by measuring point cloud using Lidar sensor, a system can create a detailed 3D maps for the car. These maps show the car where objects like other vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles are in the environment.
- Computer Aided Design (CAD) Modelling: by collecting point clouds data of real physical objects, engineer can use them as a guide to create digital models with exact dimensions and shapes.
Deep Learning for Point Clouds
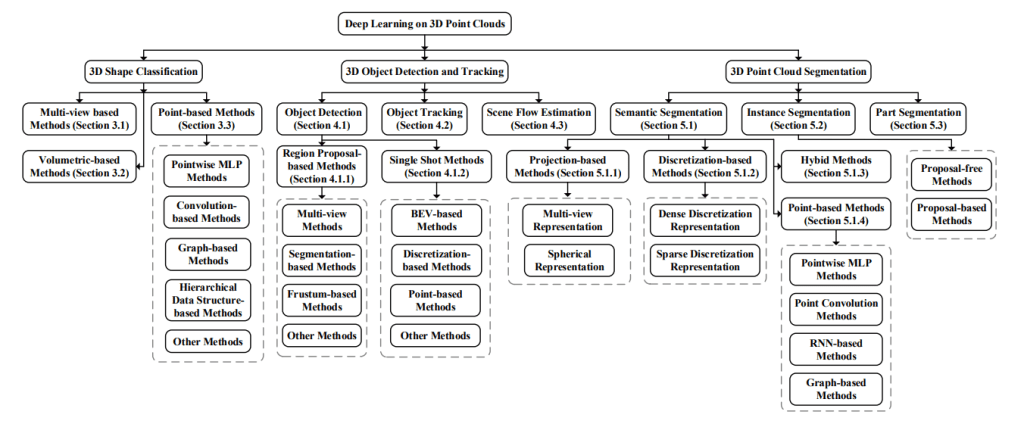
This paper [4] reviewed the common use of deep learning for point clouds. They divided the use cases into three main groups:
- Shape Classification: focuses on recognizing objects in the 3D space. Imagine a cloud of points representing an object, like a car or a tree. A deep learning algorithm will learn and identify these objects based on their unique shapes.
- Object Detection and Tracking: focuses on identifying a cluster of point cloud as object and keeping tabs on them as they move. This is important for autonomous car where the ability to track objects in real-time are crucial for safe and efficient operations.
- Segmentation: involves dividing or color coding the point cloud into meaningful segments or regions. This is similar to what is shown in Figure 1.
The full breakdown of the deep learning use cases are shown by Figure 3 below.
Summary
To conclude, a point cloud is a set of points in 3D space captured by sensors (typically Lidars) to represent an area or an object. Point cloud is used in many application, such as for self-driving car perception system, construction site, or CAD modelling. The three major deep learning use cases on point clouds are classification, segmentation, and object detection & tracking.
***
Sources:
- Geospatial World. (2023). What is a Point Cloud?. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2crAfWZOgf0
- Qi, C. R., Su, H., Mo, K., & Guibas, L. J. (2016). PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation.
- Velodyne Lidar. (2020). Title of the article or press release. Retrieved from https://velodynelidar.com/press-release/its-america-webinar-showcases-lidar-based-solutions/
- Guo, Y., Wang, C., Li, Y., Wu, C., & Yang, W. (2019). Deep Learning for 3D Point Clouds: A Survey.
Leave a reply to Project: Point Cloud Classification with PointNet – integerai.blog Cancel reply